
Cardiogenic Shock Complicating Acute Myocardial Infarction Circulation
Septic shock, the most severe complication of sepsis, carries a high mortality. Septic shock occurs in response to an inciting agent, which causes both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory immune system activation. This occurs in concert with the activation of monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils that interact with the endothelium through.

Study Tips USMLE® Step 1 Question of the Day Altered Mental State
Abstract. Sepsis-induced cardiogenic shock is a lethal condition and the management of it is challenging. Cardiogenic shock in the septic patient involves myocardial systolic and diastolic dysfunction. The limited ability of the ventricles to contract effectively results in a decrease in oxygen delivery to the organs and tissues.

Hemorrhagic Shock NEJM
In 2016, the Third International Consensus Conference for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) revised criteria for sepsis and septic shock in adults using data from nearly 150 000 patients with suspected infection in the US and Germany. 11 The Sepsis-3 definition differentiated sepsis from uncomplicated infection by the presence of life.
The Stages of Cardiogenic Shock and Its Risk Factors CVRTI
Septic shock management in the cardiac intensive care unit (CICU) is challenging due to the complex interaction of pathophysiology between vasodilatory and cardiogenic shock, complicating how to optimally deploy fluid resuscitation, vasopressors, and mechanical circulatory support devices. Because mixed shock portends high mortality and.
What is Cardiogenic Shock? Prevention & Treatment CVRT
Treatment. Shock is a state of organ hypoperfusion with resultant cellular dysfunction and death. Mechanisms may involve decreased circulating volume, decreased cardiac output, and vasodilation, sometimes with shunting of blood to bypass capillary exchange beds. Symptoms include altered mental status, tachycardia, hypotension, and oliguria.

Approach to shock Clinical sciences Osmosis Video Library
Sepsis is an increasing cause of decompensation in patients with chronic heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction. Sepsis and decompensated heart failure results in a mixed septic-cardiogenic shock that poses several therapeutic dilemmas: Rapid fluid resuscitation is the cornerstone of sepsis management, while loop diuretics are the main stay of decompensated heart failure.

Cardiogenic Shock Division of Cardiology
Abstract. Endotoxin, also referred to as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), is a potent stimulator of the inflammatory cascade which may progress to sepsis and septic shock. The term endotoxic septic shock has been used for patients who have a clinical phenotype that is characterized by high endotoxin activity in addition to a high burden of organ.

About Sepsis TORAYMYXIN™ Toray Medical Co., Ltd.
Back to the scene: what type of shock is your patient in? '-11 '-12 Restoring tissue perfusion in different types of shock DeliveryProblem Hypovolemic shock Obstruction (PE or PTX) Severeanemia Cardiogenic shock DistributionProblem Anaphylactic shock Septic Shock Neurogenic shock ExtractionProblem CO poisoning Methemoglobinemia CN poisoning.
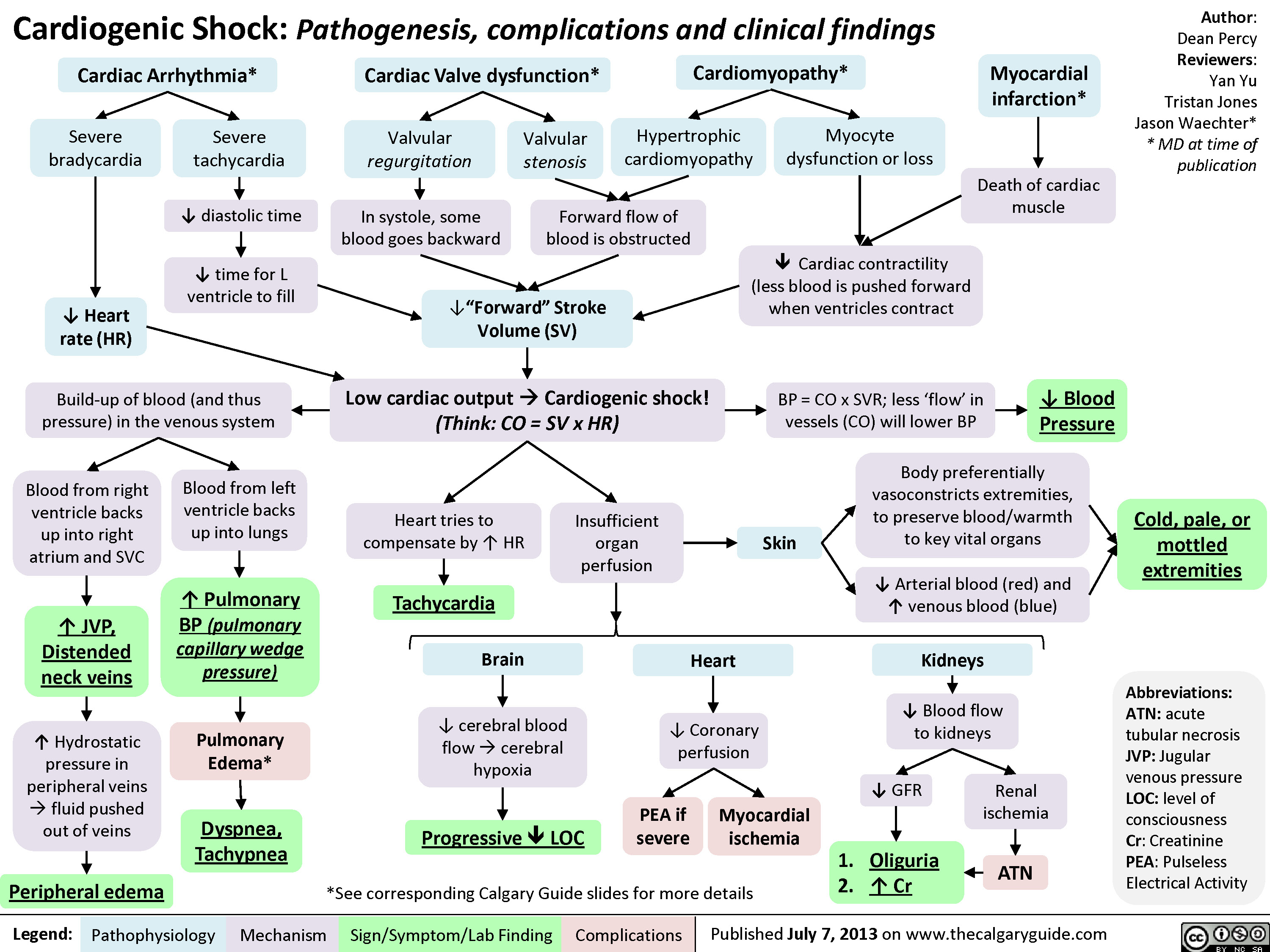
Cardiogenic Shock Calgary Guide
The epidemiology, pathophysiology, causes, and outcomes of cardiogenic shock are summarized; contemporary best medical, surgical, mechanical circulatory support, and palliative care practices are reviewed; the development of regionalized systems of care is advocated; and future research priorities are outlined.
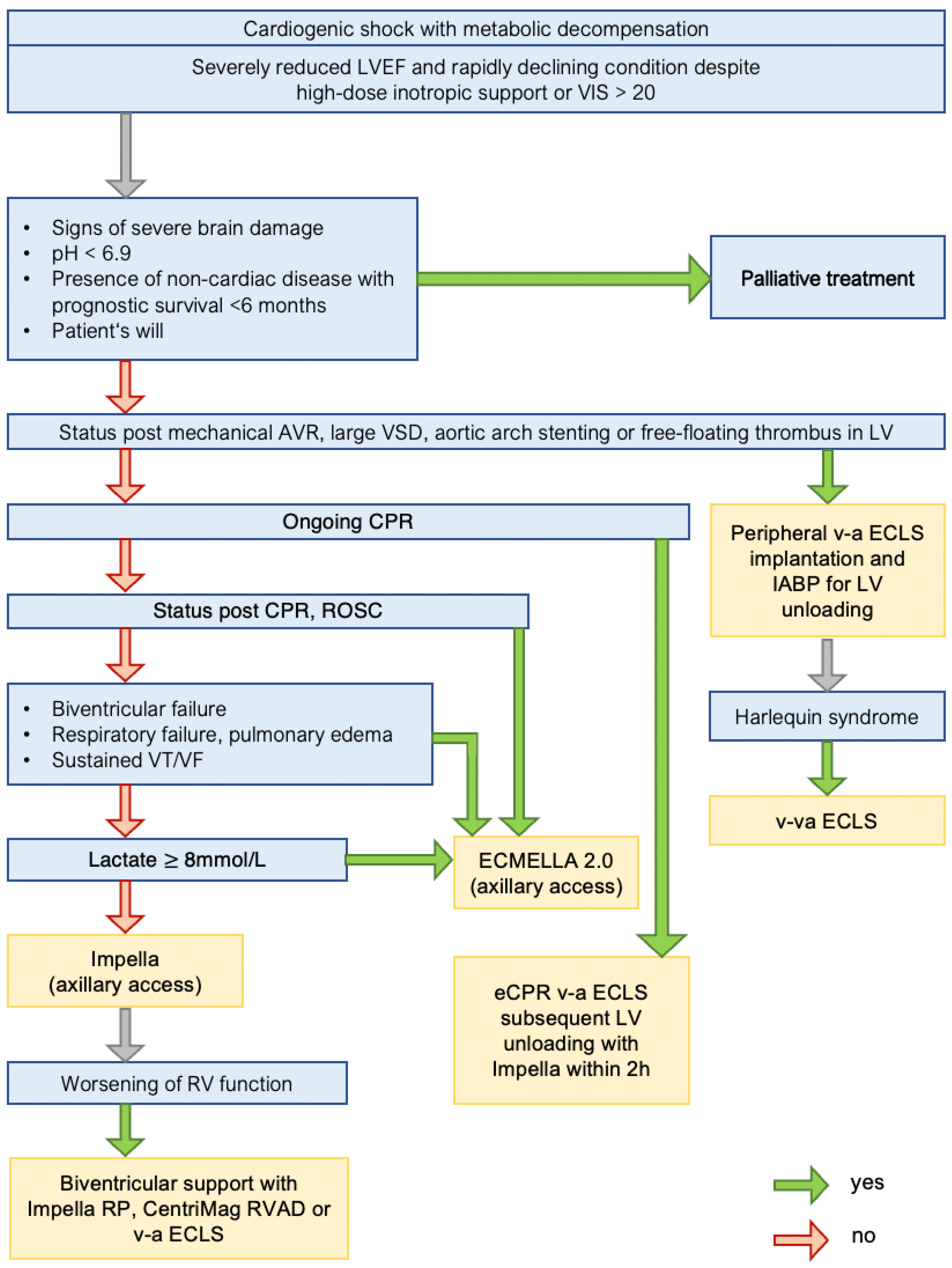
Life Free FullText Improving Survival in Cardiogenic Shock—A
Importance: Sepsis is a leading cause of death among children worldwide. Current pediatric-specific criteria for sepsis were published in 2005 based on expert opinion. In 2016, the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) defined sepsis as life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection, but it excluded children.

Circulatory Shock NEJM
Definitions and Treatment- Cardiogenic and Septic Shock. CardiogeniC ShoCk. Right ventricular failure. Criteria: organ dySfunCtion. and. Criteria: riSk of infeCtion. Pulmonary embolism. Typical signs with dyspnoea, chest pain, (pre) syncope, haemoptysis Simplified version of the Wells rule or revised Geneva score D-Dimer testing.

Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Infectious Diseases Pharmacotherapy
In the first descriptions of shock the focus was exclusively on traumatic hemorrhagic shock, but later this changed and five different types of shock came to be distinguished ().Although it is true that all types of shock can lead to the same final stage of multiorgan failure as a result of the imbalance between oxygen demand and supply, the differences in their pathogenesis and.

Cardiogenic Shock Journal of the American Heart Association
References. Hemorrhagic shock is a form of hypovolemic shock in which severe blood loss leads to inadequate oxygen delivery at the cellular level. If hemorrhage continues unchecked, death quickly.

Echocardiography in the Management of Cardiogenic Shock Manish Bansal
Main symptoms of cardiogenic shock. The main symptoms of cardiogenic shock are agitation, disturbed consciousness, cool extremities, and oliguria. Death in patients in cardiogenic shock is usually.
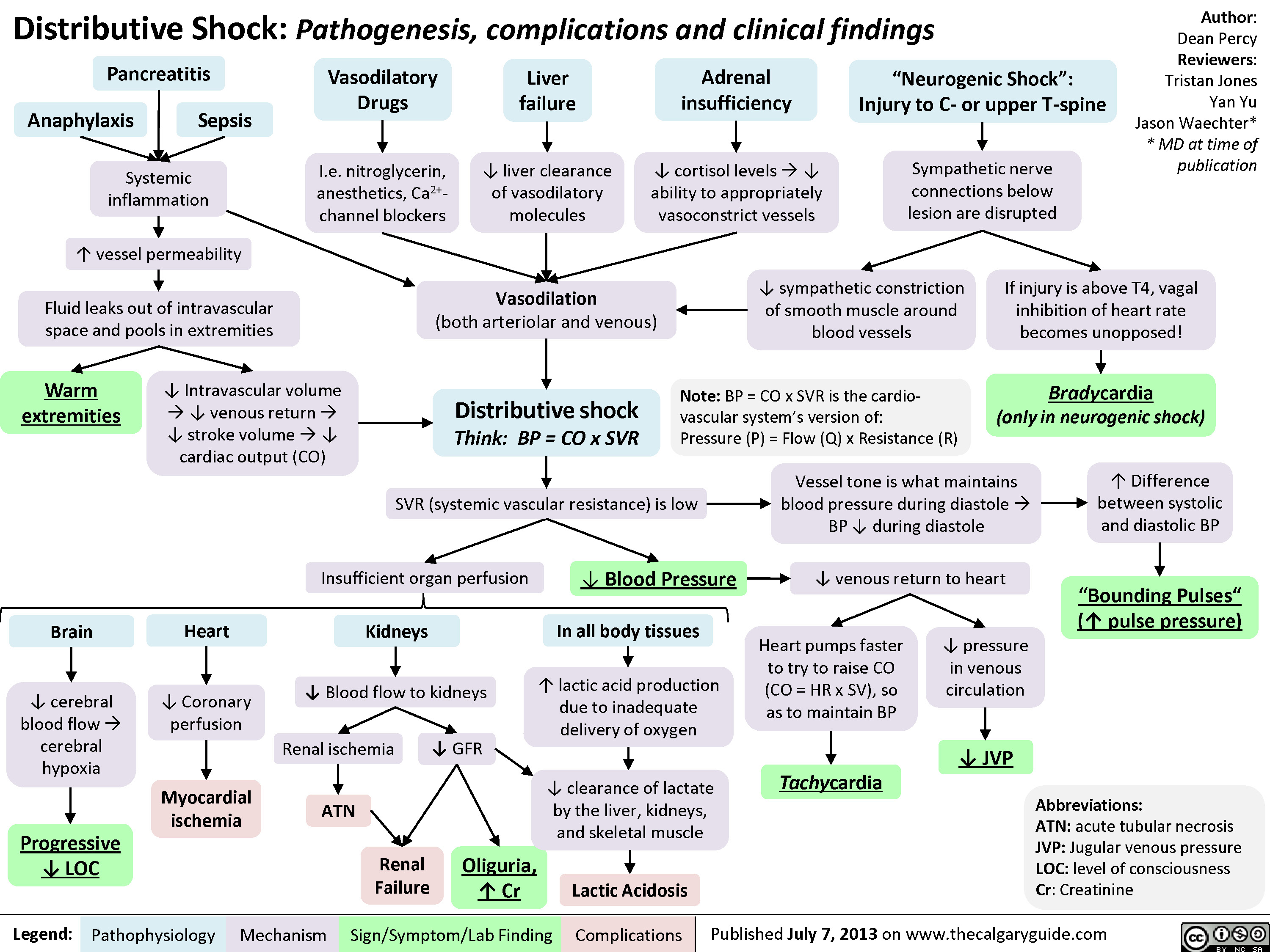
shock Calgary Guide
Securing the airway (if indicated), correcting hypoxemia, and establishing venous access for the early administration of fluids and antibiotics are priorities in the management of patients with sepsis and septic shock [ 3,4 ]. The following table summarizes emergency management of the patient with severe sepsis during the first hour ( table 1 ).

Acute Heart Failure and Cardiogenic Shock
Sepsis is the most frequent cause of vasodilatory shock, 1,2 accounting for more than 200,000 cases per year in the United States alone. Other causes include conditions in which adequate tissue.