Cell Nucleus function, structure, and under a microscope Rs' Science Eukaryotic cell

Transmission electron micrograph of an animal cell Stock Image G450/0052 Science Photo Library
Figure 3 Electron micrograph showing two cells of the bacterial species Neisseria meningitidis immunolabelled with a primary antibody that recognises an oligosaccharide, followed by a secondary antibody that has been coupled to individual 15 nm gold particles. Note that the cytoplasm has uneven electron density.. In animal cells.

Electron Micrograph Of A Plant Cell
Animal Cell Structure Animal cells are typical of the eukaryotic cell, enclosed by a plasma membrane and containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Unlike the eukaryotic cells of plants and fungi, animal cells do not have a cell wall.

Transmission electron micrograph of animal cell Stock Image G450/0051 Science Photo Library
EM tomography. Spherical protein shells of the hepatitis B virus are preserved in a thin film of ice (A) and imaged in the transmission electron microscope. Thousands of individual particles were combined by EM tomography to produce the three-dimensional
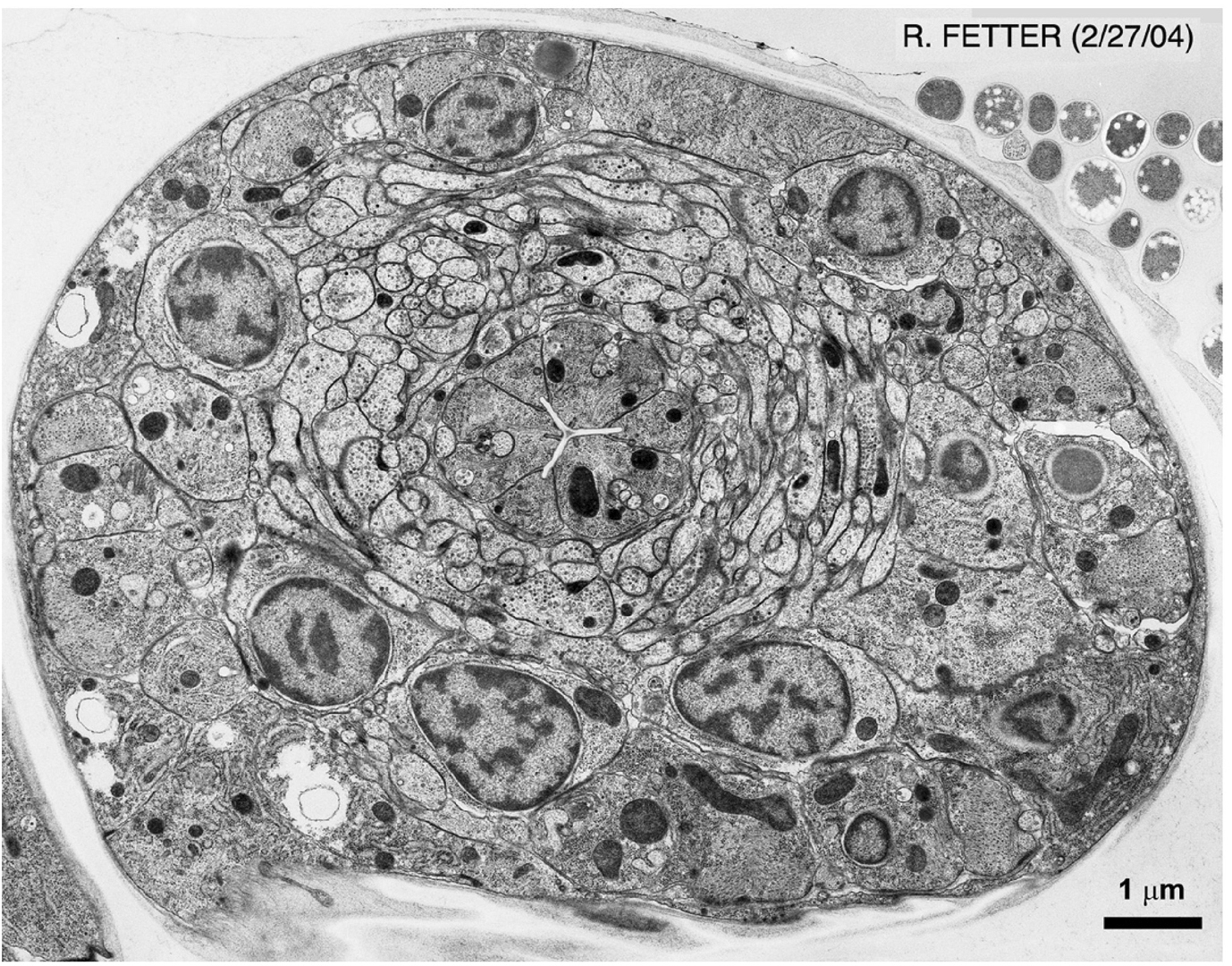
Animal Cell Tem Labeled / consider the animal cell. Which organelle is labeled I and Give
A micrograph is a photo or digital image taken through a microscope to show a magnified image of a specimen While organelles have identifying structures, specific shapes may vary depending on the location of cross-sections Prokaryotic Cell Features Feature: none nucleoid cell wall pili flagella all Eukaryotic Cell Features
.jpg)
Year 11 Bio. Key Points February 2013
In an electron micrograph of leaf cells from a quiescent desiccated dessert plant, Selaginella lepidophylla,. In animal cells they participate in spindle fiber formation during mitosis and are the point from which microtubules radiate thorough the cell to help form and maintain its shape. These structures do not involve axonemes.

Hepatocyte (liver cell) various organelles including the nucleus, lysosomes, mitochondria and
Electron micrograph of a Golgi apparatus. The Golgi apparatus consists of a stack of flattened cisternae and associated vesicles.. such as lysosomes in animal cells or vacuoles in yeast. Figure 9.27. Transport from the Golgi apparatus. Proteins are sorted in the trans Golgi network and transported in vesicles to their final destinations. In.
clothes and stuff online Animal Cell Electron Micrograph
In this video lecture, students will learn how a typical animal cell looks like an electron microscope. The students will also learn how to label different s.
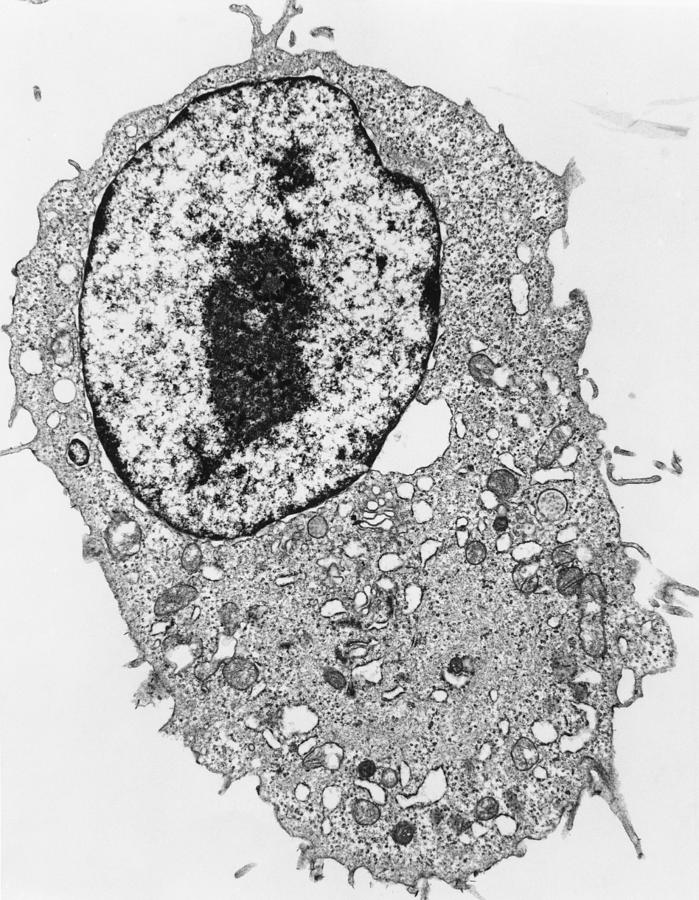
Unit 7 Microscopes & Cells Grade 6 Science
Electron Microscopy of Animal Cells Organelles under the electron microscope There are two types of electron microscope Transmission electron microscopes (TEMs) Scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) Transmission Electron Microscopes TEMs use electromagnets to focus a beam of electrons This beam of electrons is transmitted through a thin specimen

Cell Nucleus function, structure, and under a microscope Rs' Science Eukaryotic cell
Animal cell. Transmission electron micrograph of part of a mouse liver cell. In the lower frame is the cell nucleus, bound by a delicate nuclear membrane. Holes in the membrane (at right, for example) allow large molecules to pass out into the cell cytoplasm. The dark grey circles above the nucleus are mitochondria, where fats and sugars are.
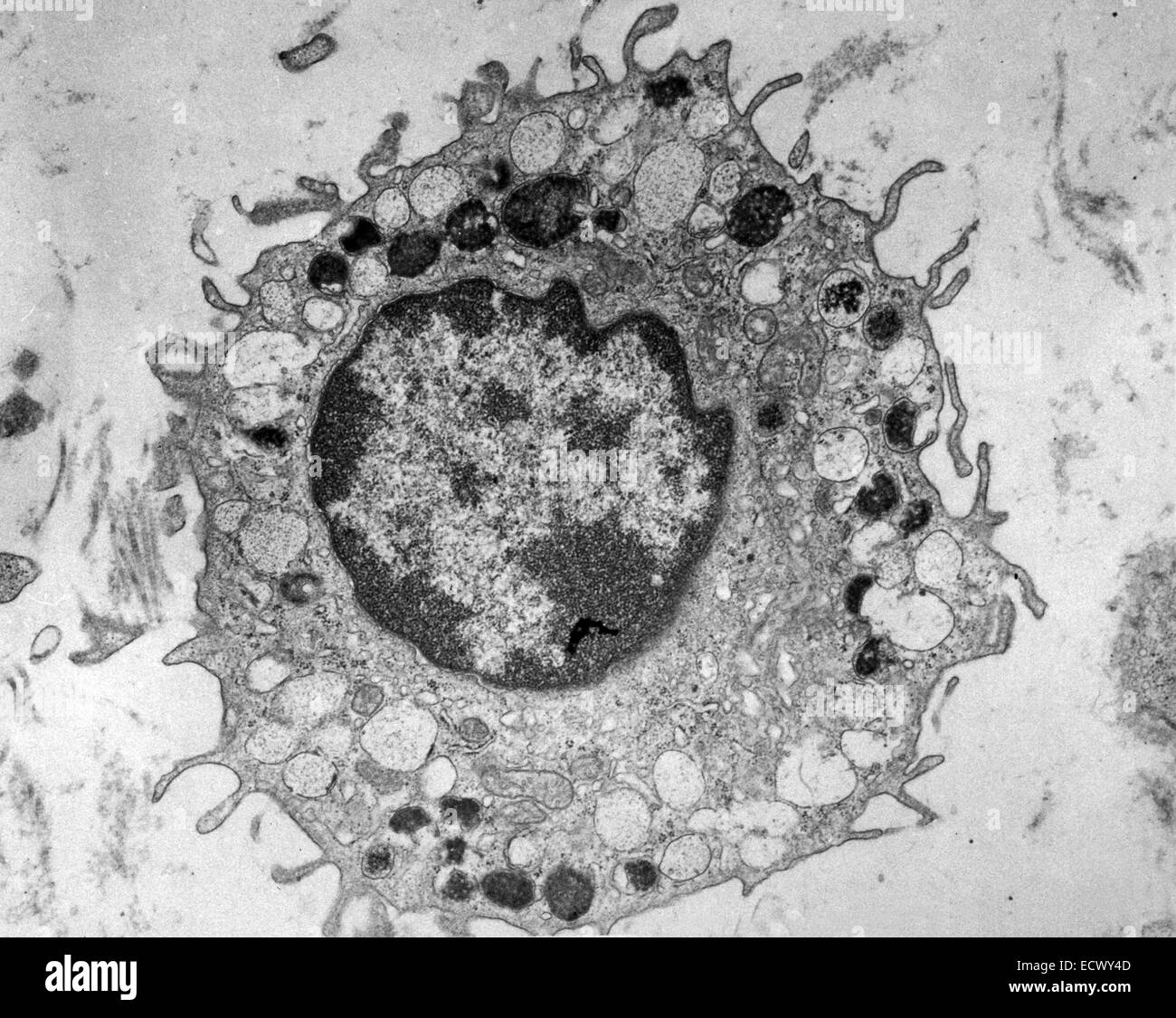
Electron micrograph of mammalian cell Stock Photo Alamy
It is responsible for controlling the cell. 2.3.3 Identify structures from 2.3.1 in electron micrographs of liver cells. Figure 2.3.2 - Electron micrograph of an animal cell 2.3.4 Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells have naked DNA which is found in the cytoplasm in a region named the nucleoid.

Cell Theory Introducing the Cell
Electron microscopy (EM) uniquely visualizes cellular structures with nanometre resolution. However, traditional methods, such as thin-section EM or EM tomography, have limitations in that they.

Biology 130 Lab 3 Electron Micrographs
The transmission electron microscope (TEM) is used to examine thin slices or sections of cells or tissues close tissue A group of similar cells that carry out the same function, eg muscle tissue..

Animal Cell Electron Microscope
Figure 2 (a) A transmission electron microscope. (b) A transmission electron micrograph of a frog leukocyte (white blood cell). The nucleus and nucleolus (Section 4.3), mitochondria (Section 4.10) and Golgi apparatus (Section 4.7) can be seen. The dark area of the nucleus contains densely packed DNA. Show description.
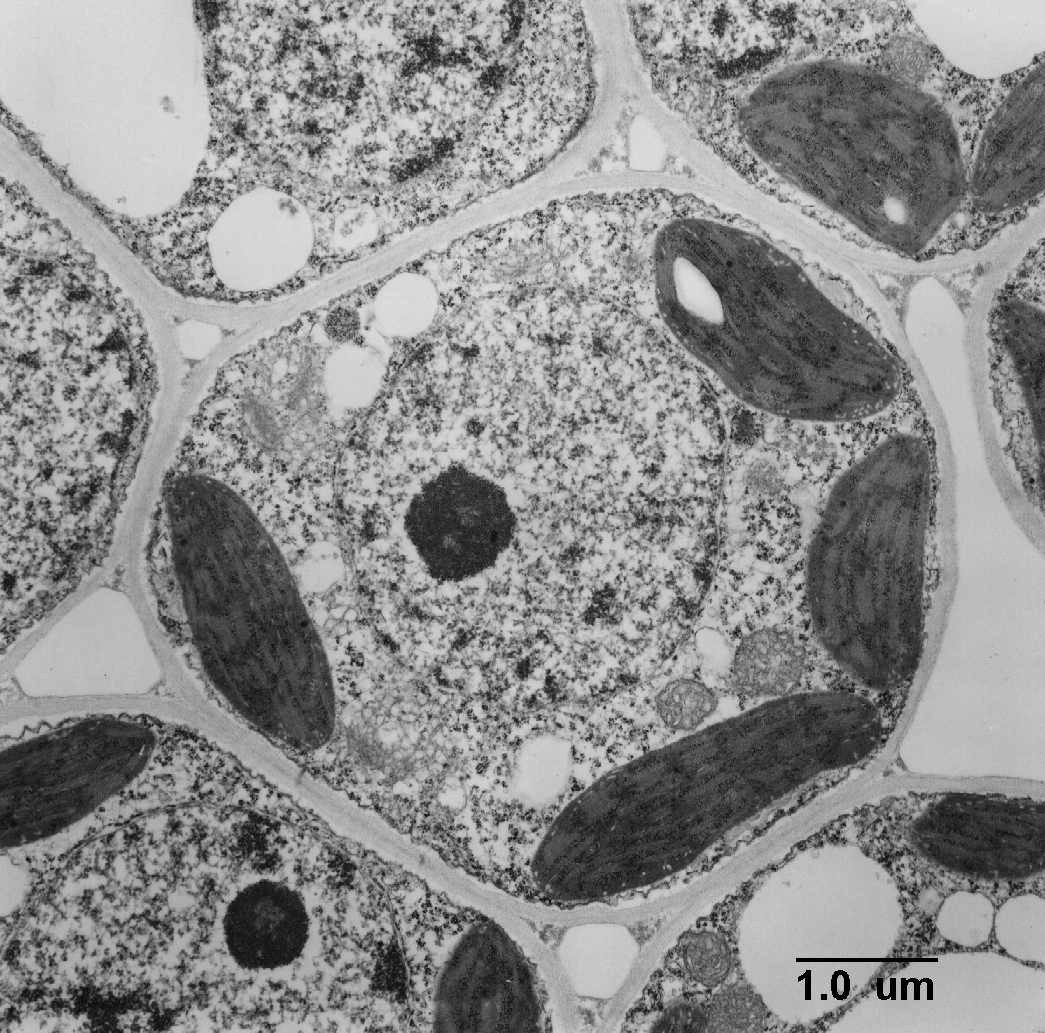
TEM of Plant Cell
Animal cell. Transmission electron micrograph of a mammalian tissue culture cell. Taking up most of the cell is the nucleus, where genes are stored in the form of chromosomes. The dark zone (centre right) in the nucleus is the nucleolus. This is the most active part of the nucleus, and contains unravelled chromosomes involved in making protein.

Solved label the ectron micrograph of an animal cell.
There are two types of electron microscope: the transmission electron microscope (TEM) is used to examine thin slices or sections of cells or tissues the scanning electron microscope.
Images 01. Introduction and Terminology Basic Human Anatomy
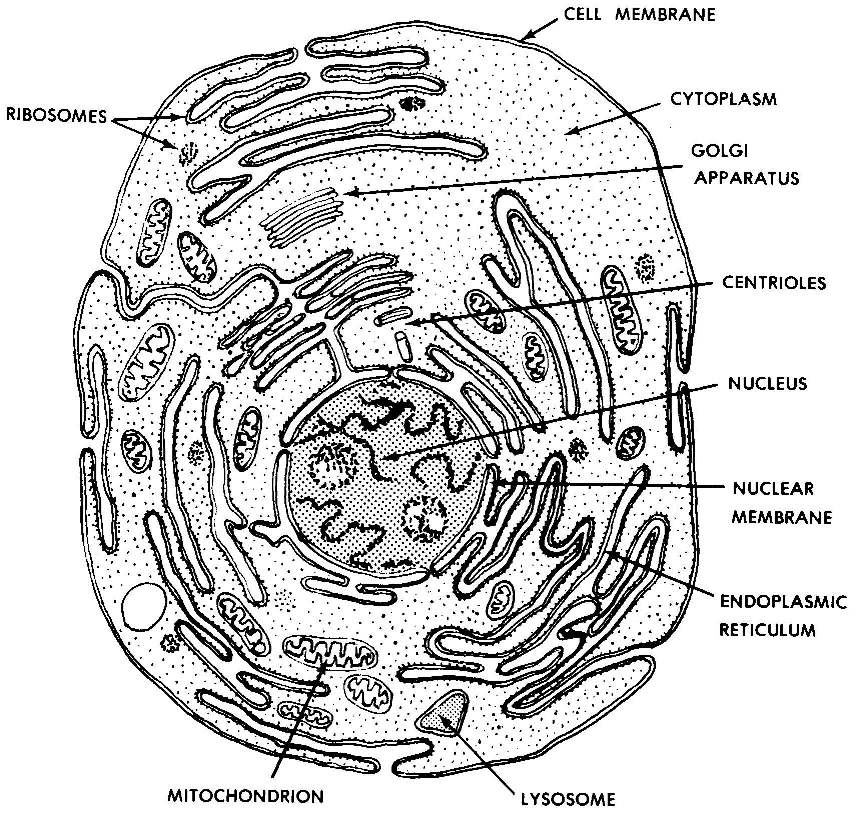
3 The Plasma Membrane 3.1 How substances move across the Plasma Membrane 4 The Cytoplasm 4.1 a) Cytosol 4.2 b) Cell inclusions 4.3 c) Organelles 4.3.1 Ribosomes 4.3.2 Endoplasmic reticulum 4.3.3 Mitochondria 4.3.4 Golgi Apparatus 4.3.5 Lysosomes 4.4 d) Microfilaments And Microtubules 5 The Nucleus 5.1 Chromosomes 6 Cell Division