Organization of the Human Nervous System The Nervous System MCAT
The Nervous System SHEN Centre for Health and Wellness
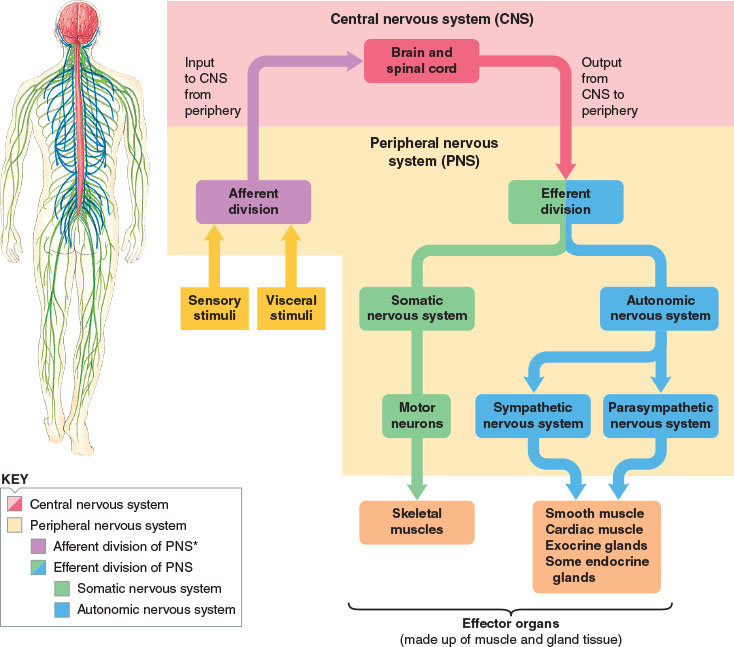
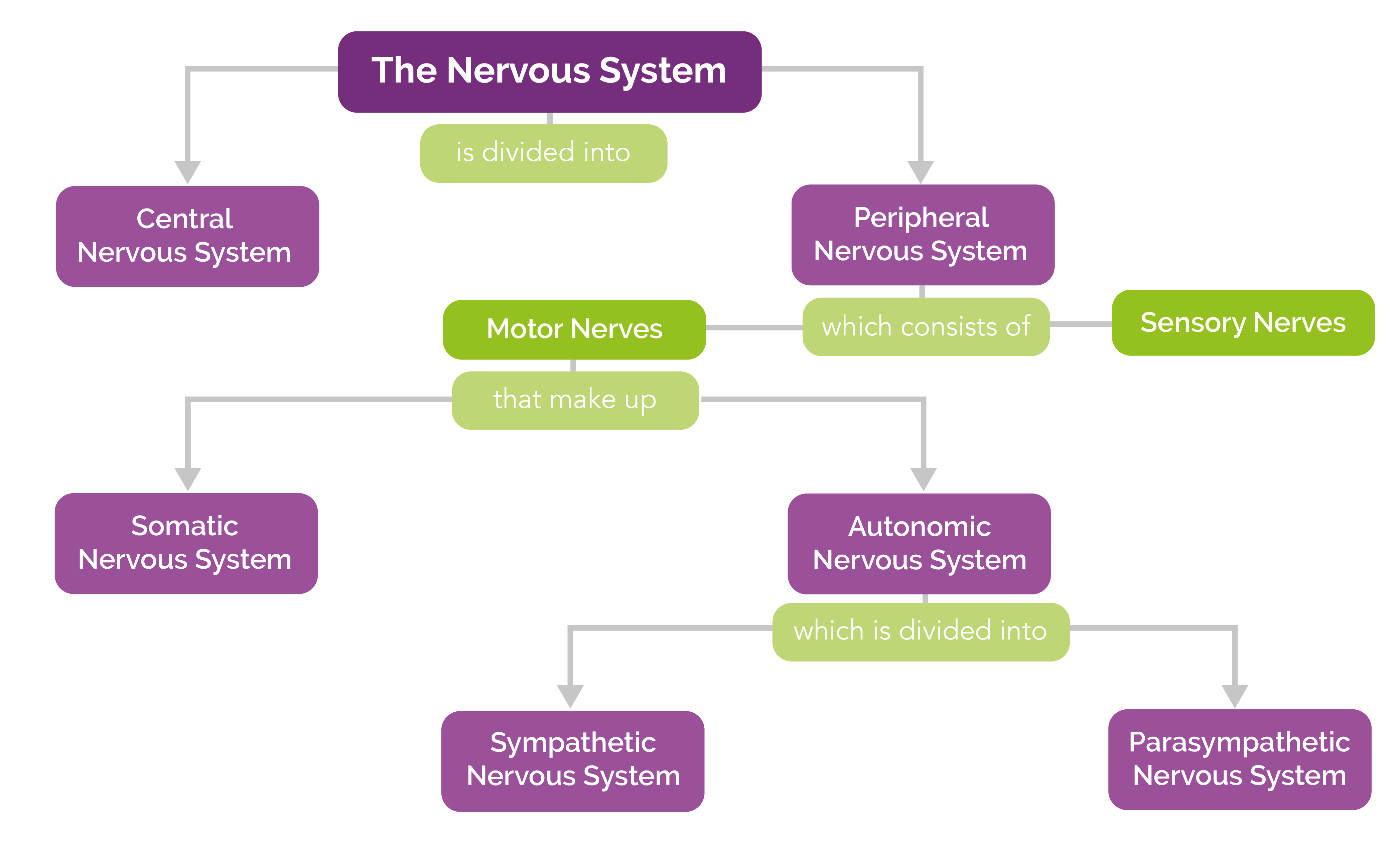
The Central Nervous System is the integration and command center of the body. It consists of the brain, spinal cord and the retinas of the eyes. The Peripheral Nervous System consists of sensory.

A diagram showing the Central Nervous System (CNS) and a flowchart
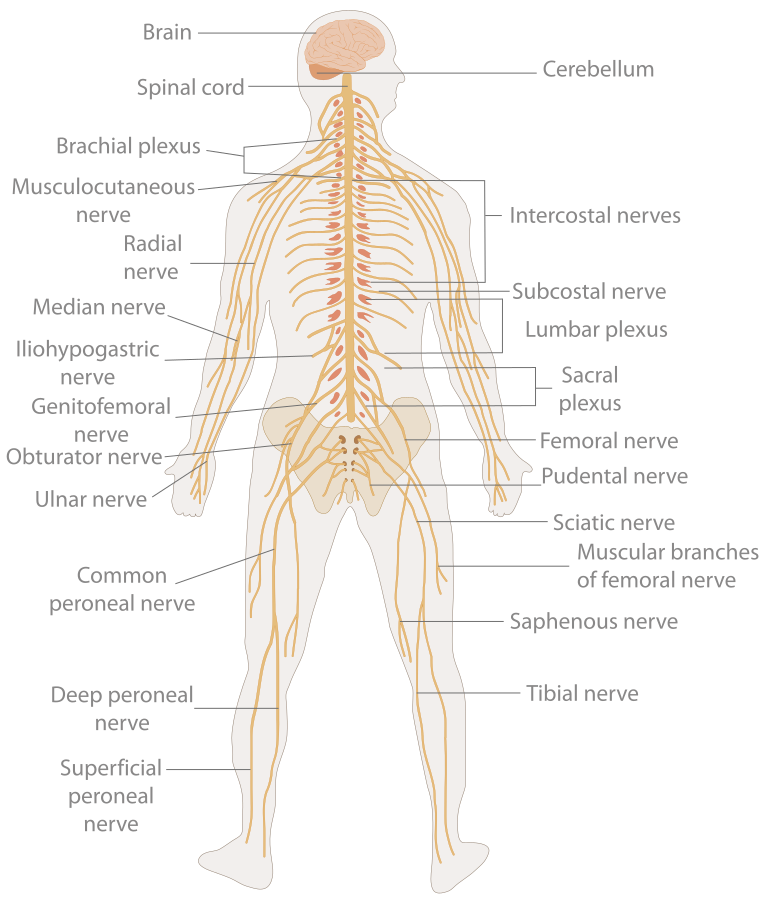
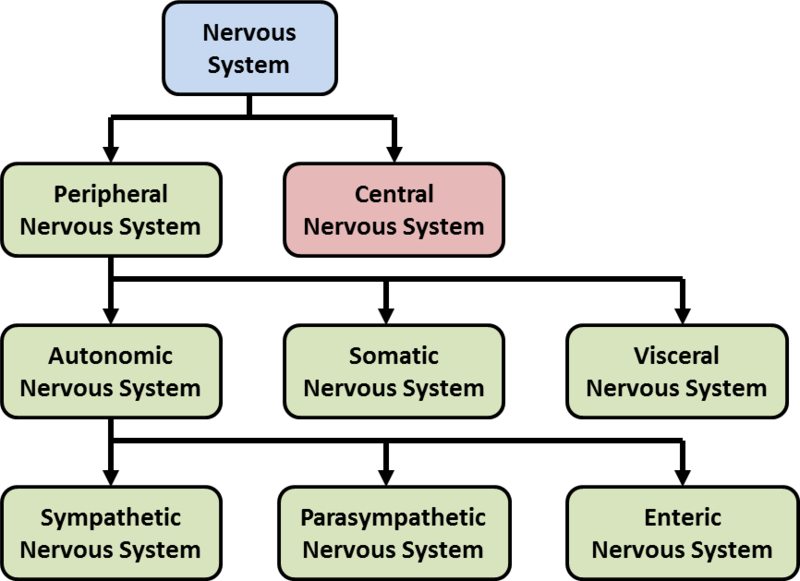
The central nervous system (CNS) is composed of the brain, spinal cord, and cerebellum. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of sensory neurons, motor neurons, and neurons that communicate either between subdivisions of the PNS or connect the PNS to the CNS. The Human Nervous System: The major organs and nerves of the human nervous system.
Organization of the Human Nervous System The Nervous System MCAT
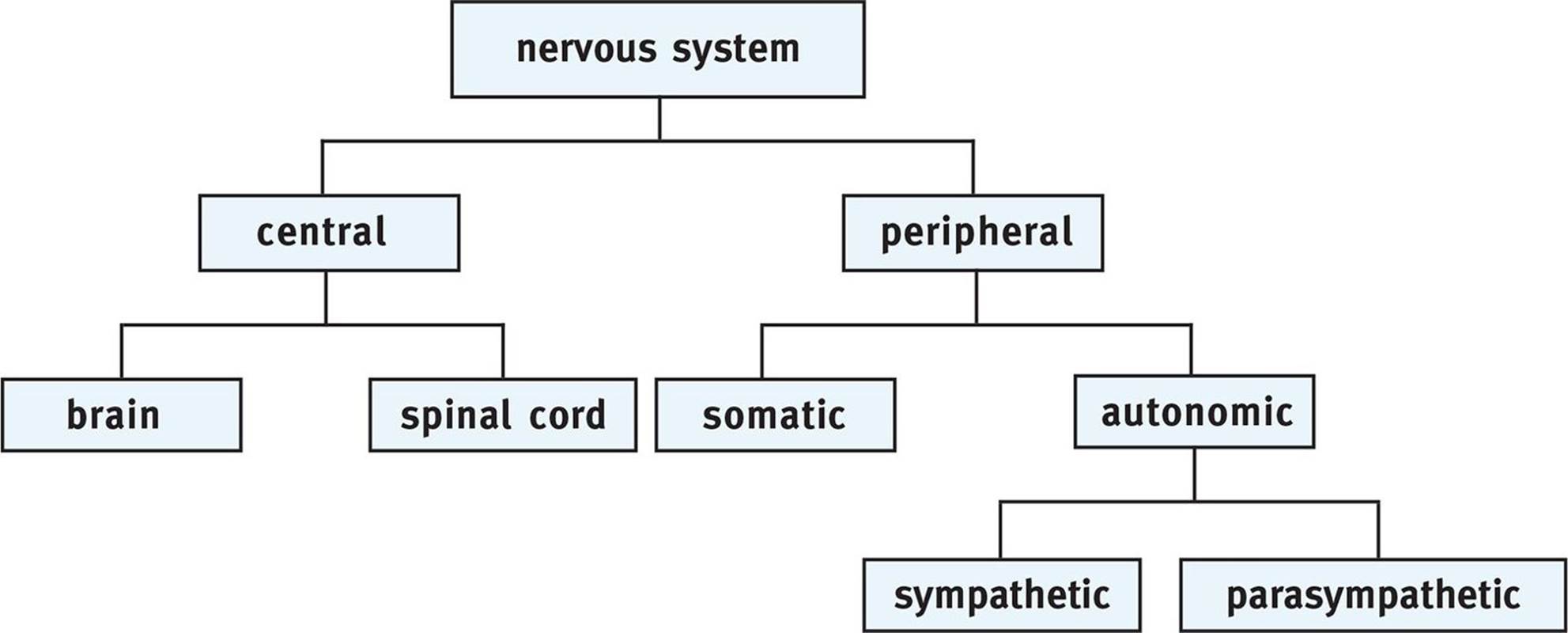
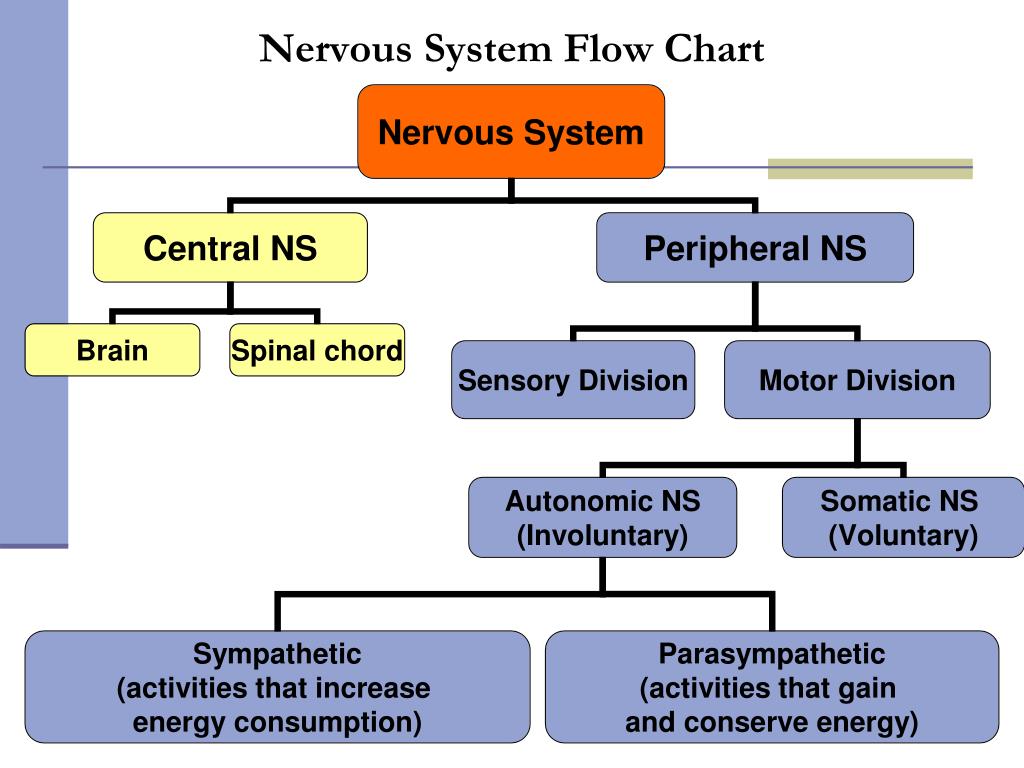
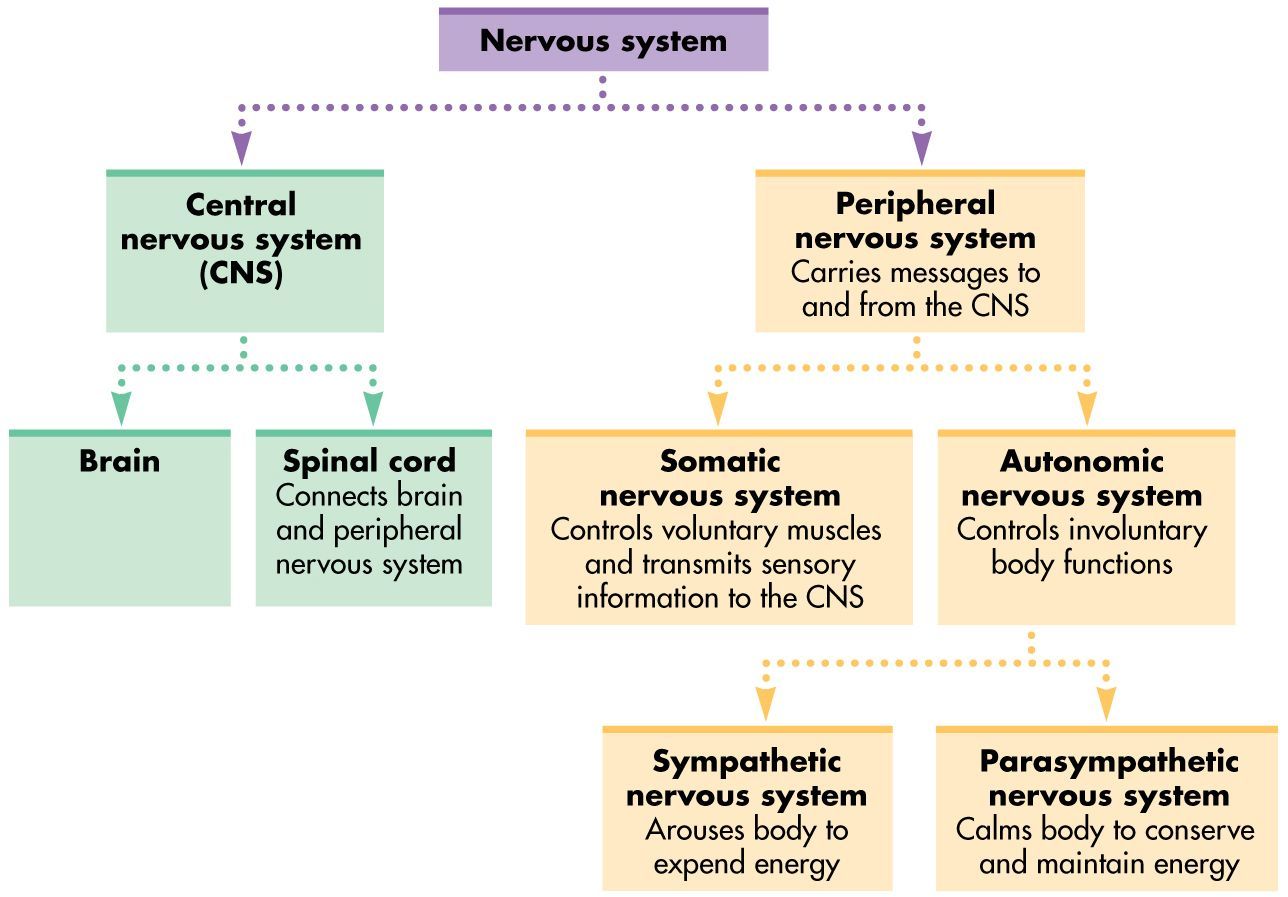
Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) (Brain & Spinal Cord) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) (Cranial & Spinal Nerves ) Sensory Division (Afferent) Motor Division (Efferent) Voluntary or Somatic Nerves Involuntary or Au tonomic Nerves Sympathetic Parasympathetic Nervous System Flow Chart . Title: Nervous System Flow Chart.PDF
8.2 Introduction to the Nervous System Human Biology
The central system is the primary command center for the body, and is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system consists of a network of nerves that connects the rest.
human nervous system flowchart
Flowchart nodes. Peripheral Nervous System - nerve processes that connect the CNS with glands, muscles and receptors. (cranial and spinal nerves) Somatic Nervous System - Carry impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscle tissue (voluntary) Autonomic Nervous System - Carries info from the CNS to cardiac muscle, glands, and smooth muscle (involuntary)

Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Parts and Function
Nervous system anatomy and physiology. Neuron action potential. Anatomy and physiology of the eye. Anatomy and physiology of the ear. Osmosis Anatomy and Physiology of the Nervous System high-yield notes offers clear overviews with striking illustrations, tables, and diagrams. Make learning more manageable.

organization of nervous system flowchart organization of the nervous
Table 11.2.1 11.2. 1: Name of structures depend on the location. A group of neuron cell bodies within the gray matter is called a nucleus in the CNS and a ganglion in the PNS. A bundle of axon within the white matter is called a tract or column in the CNS, and a nerve or nerve fiber in the PNS. CNS.

Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology Nervous system, Nclex and
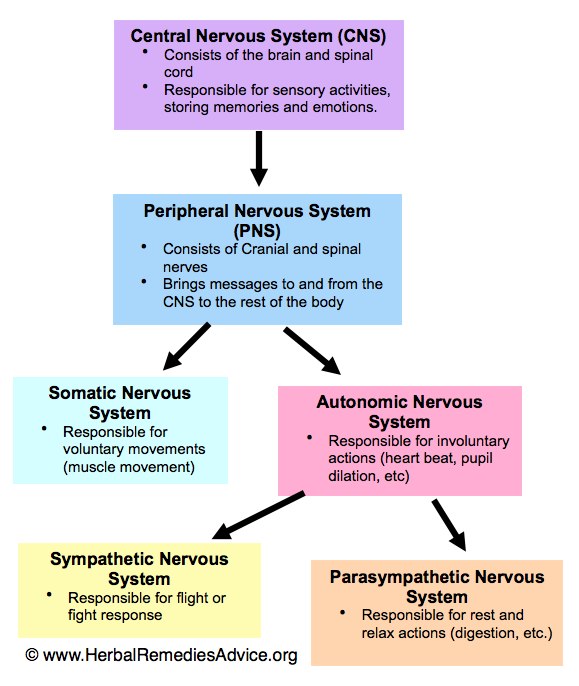
The nervous system has two main parts: Central nervous system (CNS) : Your brain and spinal cord make up your CNS. Your brain reads signals from your nerves to regulate how you think, move and feel. Peripheral nervous system (PNS): Your PNS is made up of a network of nerves. The nerves branch out from your spinal cord.
Nervous System Diagram, Function & Diseases StudiousGuy
The nervous system is the most complex body system !! Constantly alive with electricity, the. system is the body's prime communication coordination network. It is so vast and complex that, estimate is that all the individual from one body, joined end to reach around the world two and times. The Brain and Spinal Cord are Nervous System.

How Does the Nervous System Maintain Homeostasis Biology Dictionary
An Overview of the Nervous System. Listen to the Audio. Now that we have looked at the cells that make up the nervous system and ways in which they process and communicate information, take a look at Figure 2.5. This figure shows the organization of the various parts of the nervous system and will help in understanding how all the different.
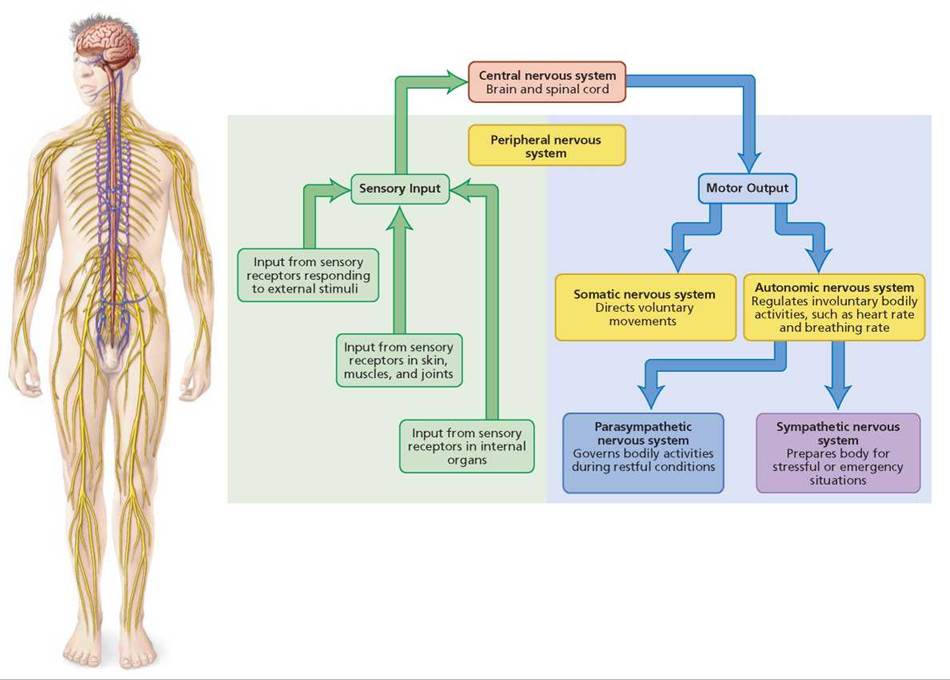
FIGURE 8.1. An overview of the nervous system. The various parts of the
In the human body, the neural system integrates the activities of organs based on the stimuli, which the neurons detect and transmit. They transmit messages in the form of electrical impulses and convey messages to and from the sense organs. Thus, the nervous coordination involves the participation of the sense organs, nerves, spinal cord, and.
Structure of the Nervous System
The nervous system produces a response in effector organs (such as muscles or glands) due to the sensory stimuli. The motor ( efferent) branch of the PNS carries signals away from the CNS to the effector organs. When the effector organ is a skeletal muscle, the neuron carrying the information is called a somatic motor neuron; when the effector.
Nervous system MEpedia
It has multiple divisions, beginning with its two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), as shown in Figure 11.2.4 11.2. 4. The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord, and the PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are bundles of axons from neurons. The nerves of the PNS connect the CNS to the rest.
Nervous System Explained Chiropractic Wellness Centre Leicestershire
The nervous system is a network of neurons whose main feature is to generate, modulate and transmit information between all the different parts of the human body. This property enables many important functions of the nervous system, such as regulation of vital body functions ( heartbeat, breathing, digestion), sensation and body movements.

Structure of the Nervous System Psychology tutor2u
1 / 4. Find step-by-step Anatomy and physiology solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Create a flowchart that shows the main components or structures of the nervous system and each of its subdivisions. List the functions and processes that each component controls..
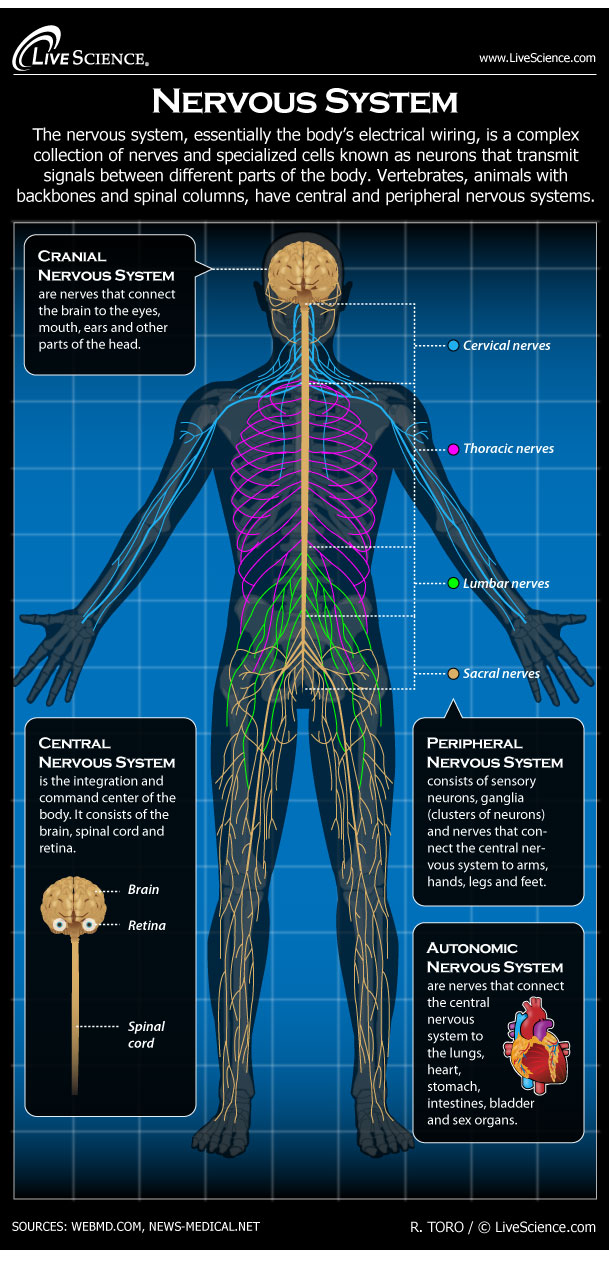
Human Nervous System Diagram How It Works Live Science
Flowchart illustrating the human nervous system. Learn how the nerves and the cells carry messages to and from the brain with this nervous system flowchart. You can easily edit this template using Creately. You can export it in multiple formats like JPEG, PNG and SVG and easily add it to Word documents, Powerpoint (PPT) presentations, Excel or.