
Rheumatologic conditions associated with cardiogenic shock Download
Impella versus extracorporal life support in cardiogenic shock: a propensity score adjusted analysis. ESC Heart Fail. 2021 Apr;8 (2):953-961. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13200. Epub 2021 Feb 9.
Life Free FullText Improving Survival in Cardiogenic Shock—A
Impella versus extracorporal life support in cardiogenic shock: a propensity score adjusted analysis. Bernhard Wernly, Mina Karami, Annemarie E. Engström, Stephan Windecker, Lukas Hunziker, Thomas F. Lüscher,.
Cureus Mechanical Assist DeviceAssisted Percutaneous Coronary
Patients receiving Impella versus ECLS (extracorporal life support) with regard to baseline characteristics, feasibility, and outcomes in CS are compared. The mortality in cardiogenic shock (CS) is high. The role of specific mechanical circulatory support (MCS) systems is unclear. We aimed to compare patients receiving Impella versus ECLS (extracorporal life support) with regard to baseline.

Impella versus extracorporal life support in cardiogenic shock a
Wernly B, Karami M, Engström AE, Windecker S, Hunziker L, Lüscher TF et al. Impella versus extracorporal life support in cardiogenic shock: a propensity score adjusted analysis. ESC heart failure . 2021 Apr;8(2):953-961.
Frontiers Ventricular Unloading Using the ImpellaTM Device in
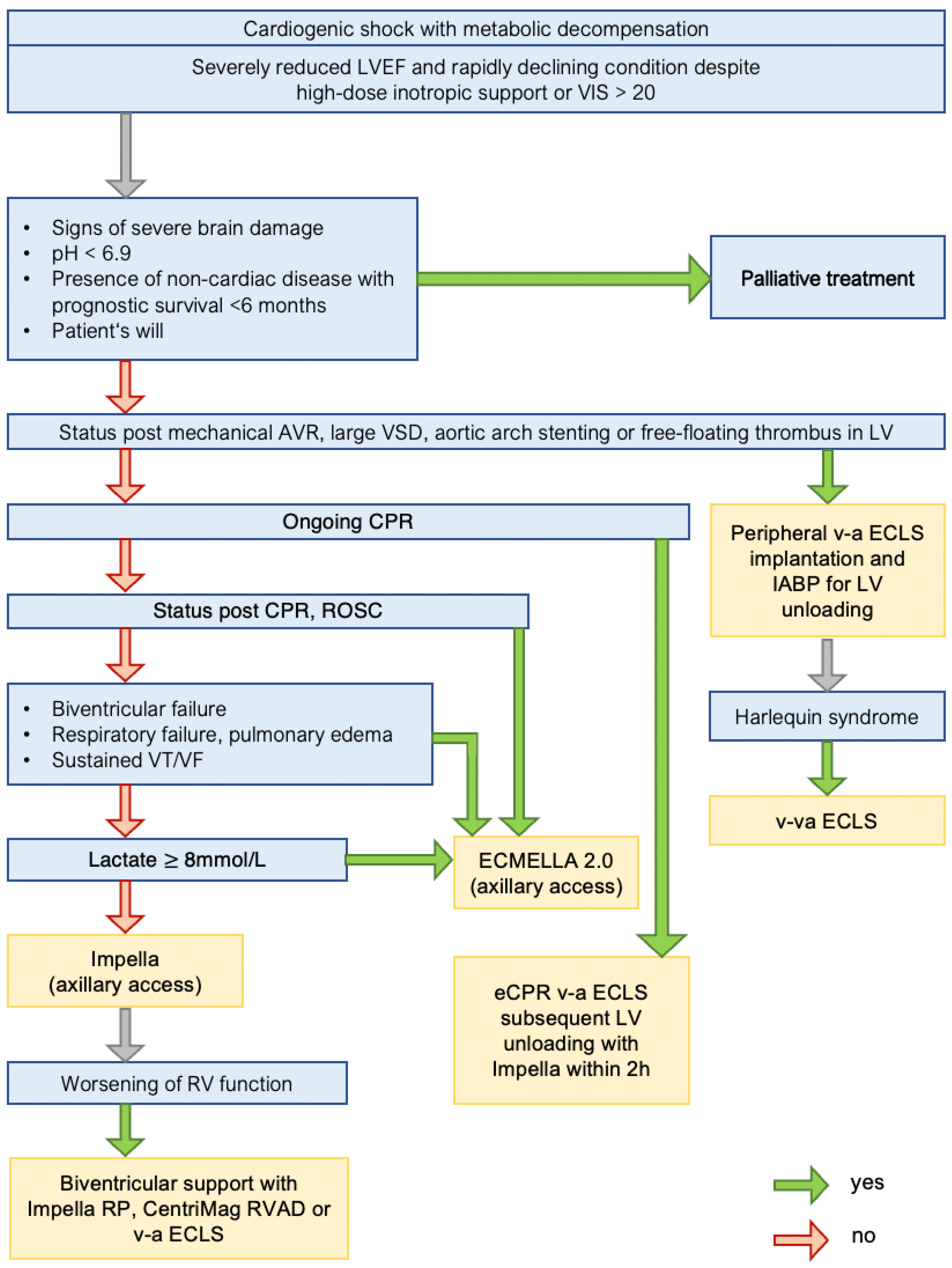
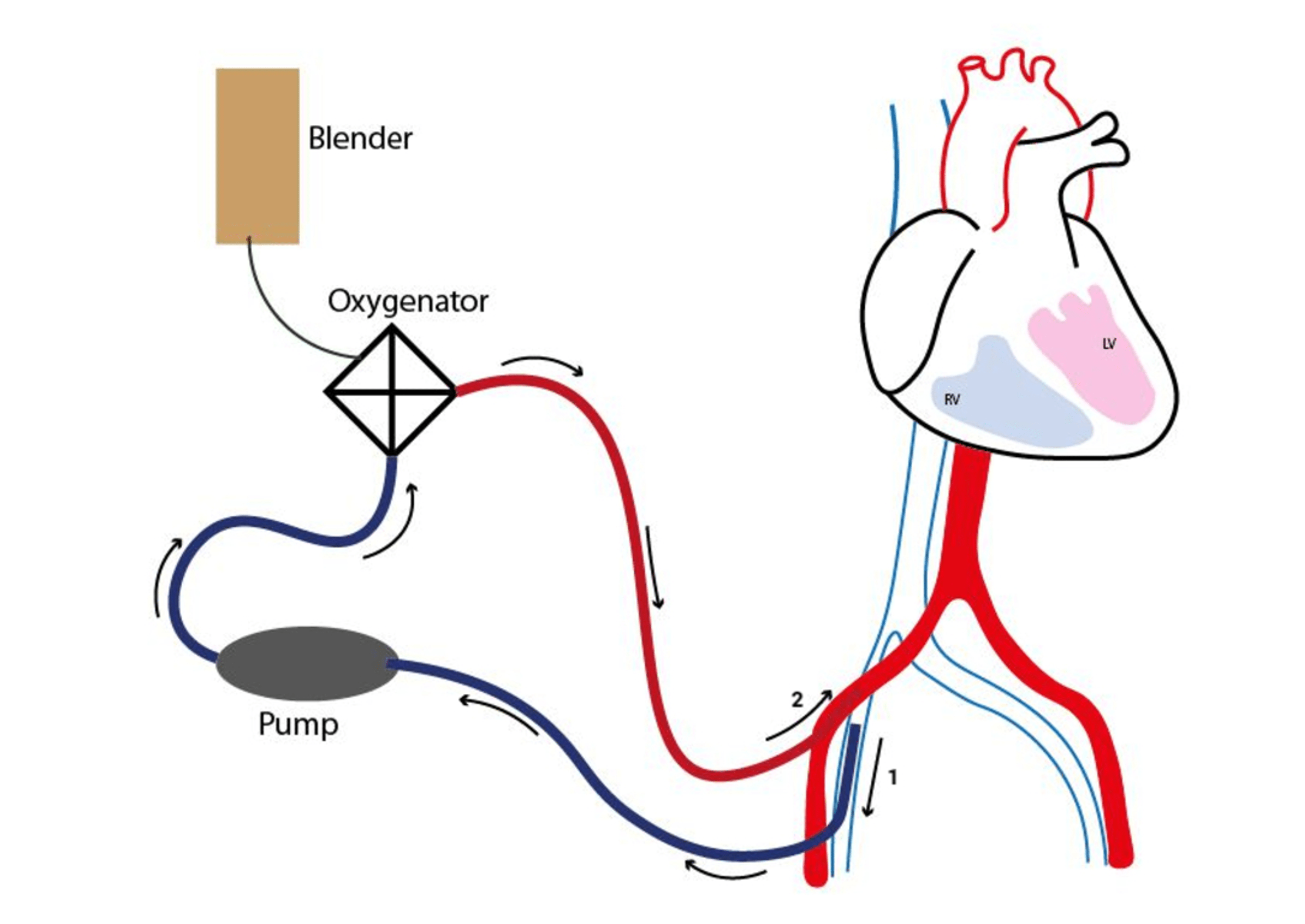
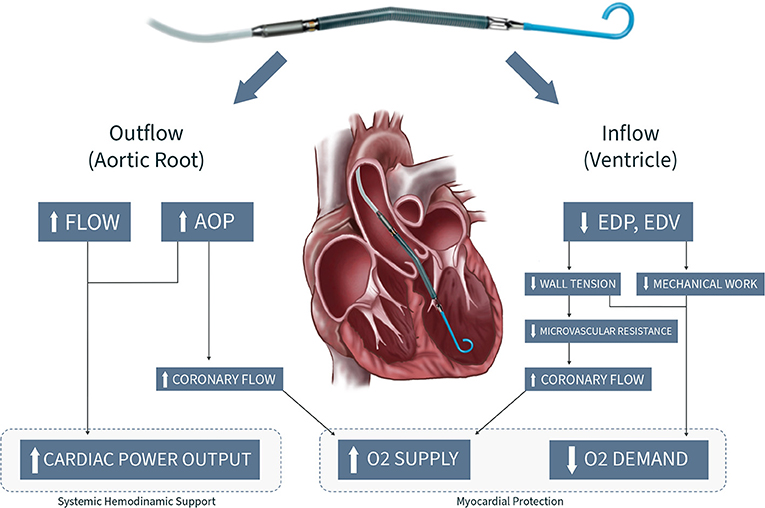
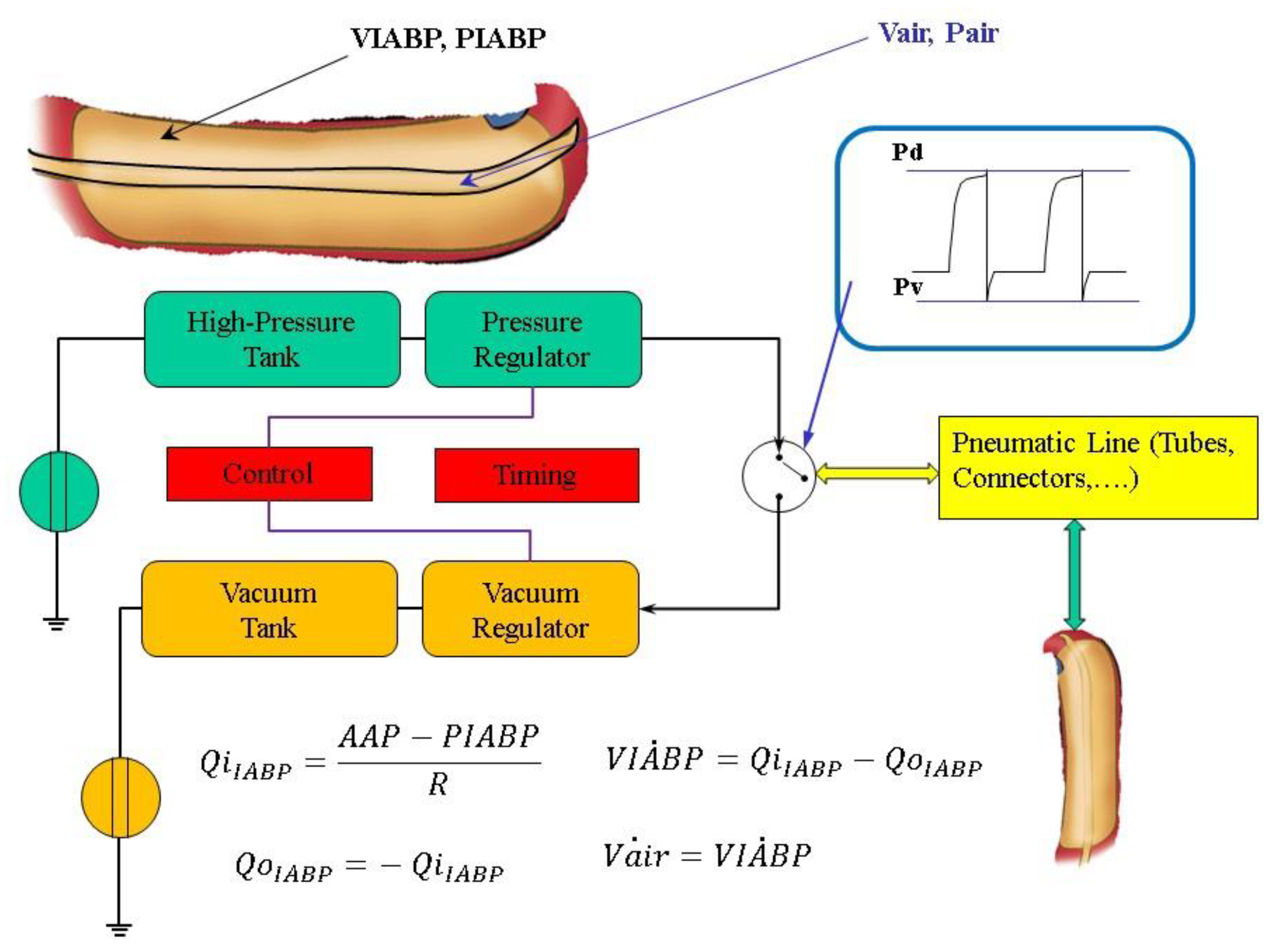
INTRODUCTION. Mechanical circulatory support (MCS) has been used for the treatment of cardiogenic shock (CS) since the early 1960s [].In recent years, technological advances have revolutionized the field of extracorporeal life support (ECLS), offering more reliable and miniature devices that can provide prolonged haemodynamic support and may improve patient outcomes [].

Extracorporeal Life Support for Cardiac Arrest and Cardiogenic Shock
Our aim was to compare the outcomes of Impella with extracorporeal life support (ECLS) in patients with post-cardiac arrest cardiogenic shock (CS) complicating acute myocardial infarction (AMI). This was a retrospective study of patients resuscitated from out of hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) with p.

Figure 1 from Minimally invasive CentriMag ventricular assist device
Our aim was to compare the outcomes of Impella with extracorporeal life support (ECLS) in patients with post-cardiac arrest cardiogenic shock (CS) complicating acute myocardial infarction (AMI). This was a retrospective study of patients resuscitated.

Extracorporeal life support Anesthesia Key
On the other hand, studies focusing on ECLS in patients with post-cardiac arrest CS yielded conflicting results [8][9][10]. Moreover, studies comparing Impella and ECLS in large homogenous patient.

Percutaneous Circulatory Support in Cardiogenic Shock Circulation
Impella versus extracorporal life support in cardiogenic shock: a propensity score adjusted analysis Bernhard Wernly1,2* , Mina Karami3, Annemarie E. Engström4.

Extracorporeal lifesupport in patients requiring CPR The Lancet
Impella versus extracorporal life support in cardiogenic shock: a propensity score adjusted analysis B Wernly, M Karami, Annemarie Engström, S Windecker, L Hunziker, TF Luscher, JP Henriques, MW Ferrari, S Binnebossel, M Masyuk, D Niederseer, P Abel, G Fuernau, M Franz, M Kelm, MC Busch, SB Felix, H Thiele, A Lauten, C Jung

Extracorporeal life support The BMJ
Introduction. Cardiogenic shock (CS) is still associated with a high mortality rate, especially after cardiac arrest. 1, 2 CS due to acute myocardial infarction (AMI-CS) and cardiac arrest CS (CA-CS) constitute the two major causes of the disease. 3 Despite advances in medical management including the administration of inotropes, vasopressors, and the introduction of dedicated shock teams.

Figure 1 from Cardiogenic shock From ECMO to Impella and beyond
Impella versus extracorporal life support in cardiogenic shock: a propensity score adjusted analysis. February 2021 · ESC Heart Failure. Bernhard Wernly; Mina Karami; Annemarie E Engström.
JCDD Free FullText IABP Versus Impella Support in Cardiogenic
Aims The mortality in cardiogenic shock (CS) is high. The role of specific mechanical circulatory support (MCS) systems is unclear. We aimed to compare patients receiving Impella versus ECLS (extrac.
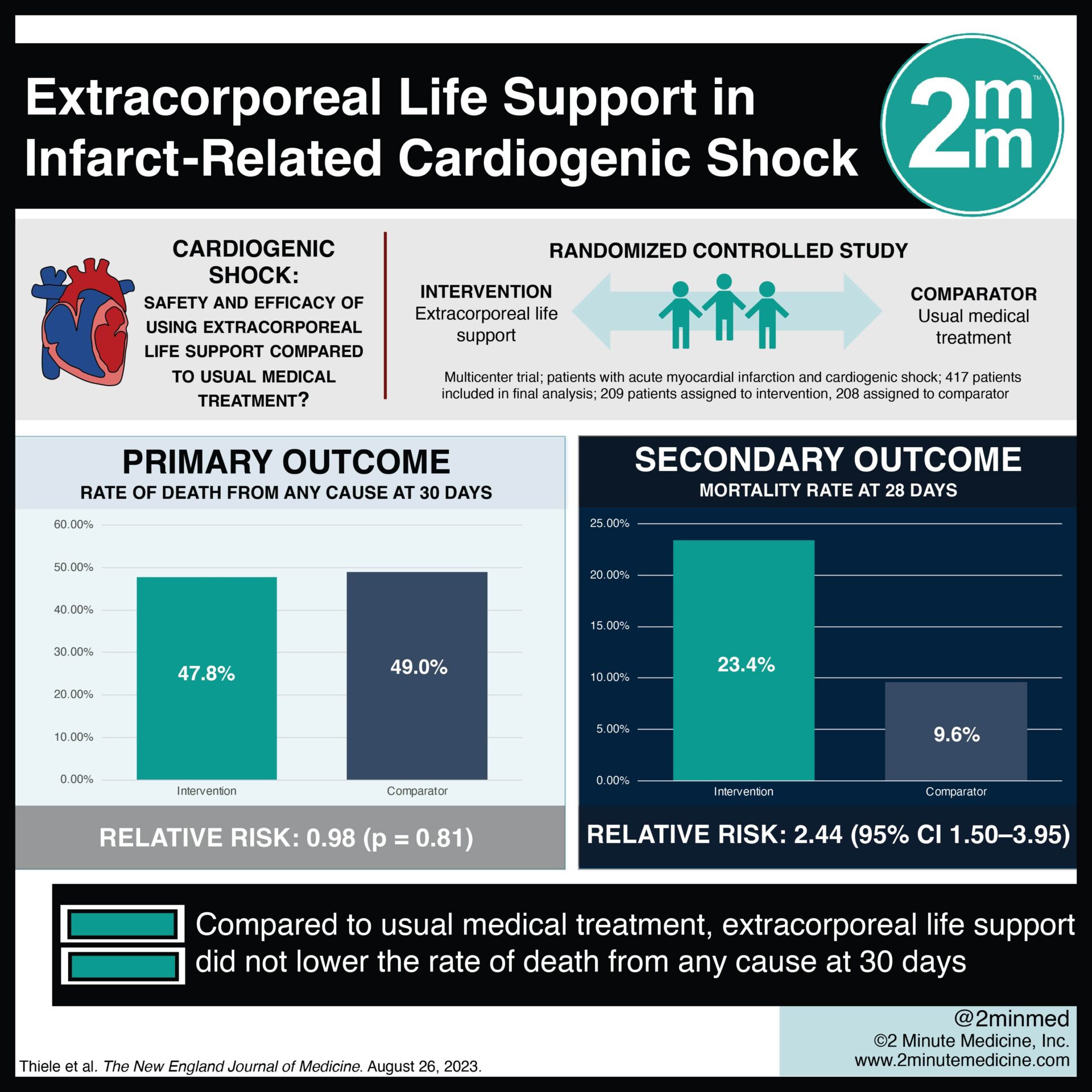
VisualAbstract Extracorporeal Life Support in InfarctRelated
Impella versus extracorporal life support in cardiogenic shock: a propensity score adjusted analysis Bernhard Wernly, Mina Karami, Annemarie E. Engström, Stephan Windecker, Lukas Hunziker, Thomas F. Lüscher, Jose P. Henriques, Markus W. Ferrari, Stephan Binnebößel, Maryna Masyuk,.
(PDF) Impella versus extracorporal life support in cardiogenic shock a
AIMS The mortality in cardiogenic shock (CS) is high. The role of specific mechanical circulatory support (MCS) systems is unclear. We aimed to compare patients receiving Impella versus ECLS (extracorporal life support) with regard to baseline characteristics, feasibility, and outcomes in CS. METHODS AND RESULTS This is a retrospective cohort study including CS patients over 18 years with a.

Extracorporeal Life Support in InfarctRelated Cardiogenic Shock NEJM
Impella versus extracorporal life support in cardiogenic shock: a propensity score adjusted analysis. Authors: Bernhard Wernly Mina Karami Annemarie E Engström Stephan Windecker Lukas Hunziker Thomas F Lüscher Jose P Henriques Markus W Ferrari Stephan Binnebößel Maryna Masyuk David Niederseer Peter Abel Georg Fuernau Marcus Franz Malte Kelm.